Maternal and Fetal Mitochondrial Gene Dysregulation in Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy
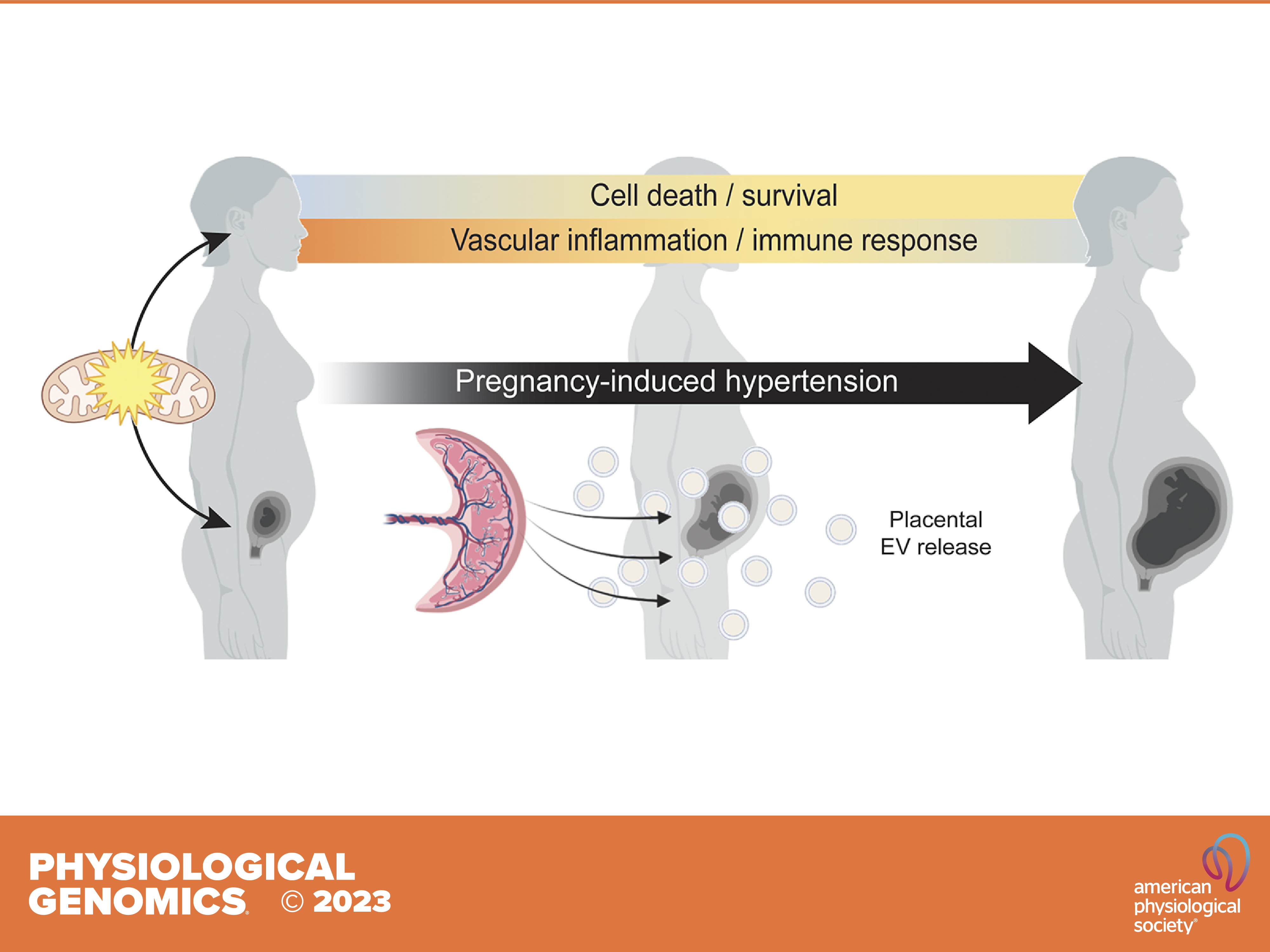
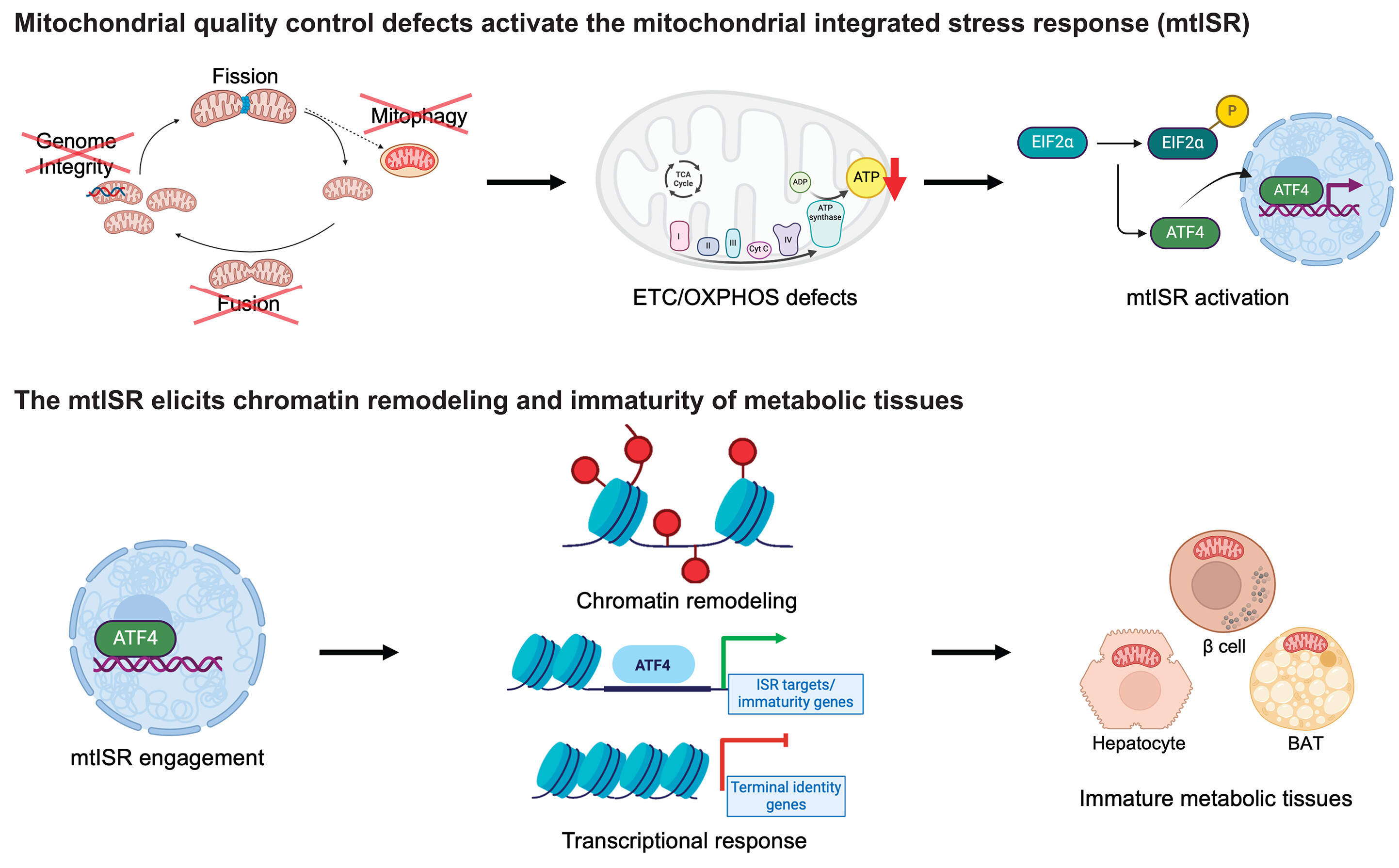
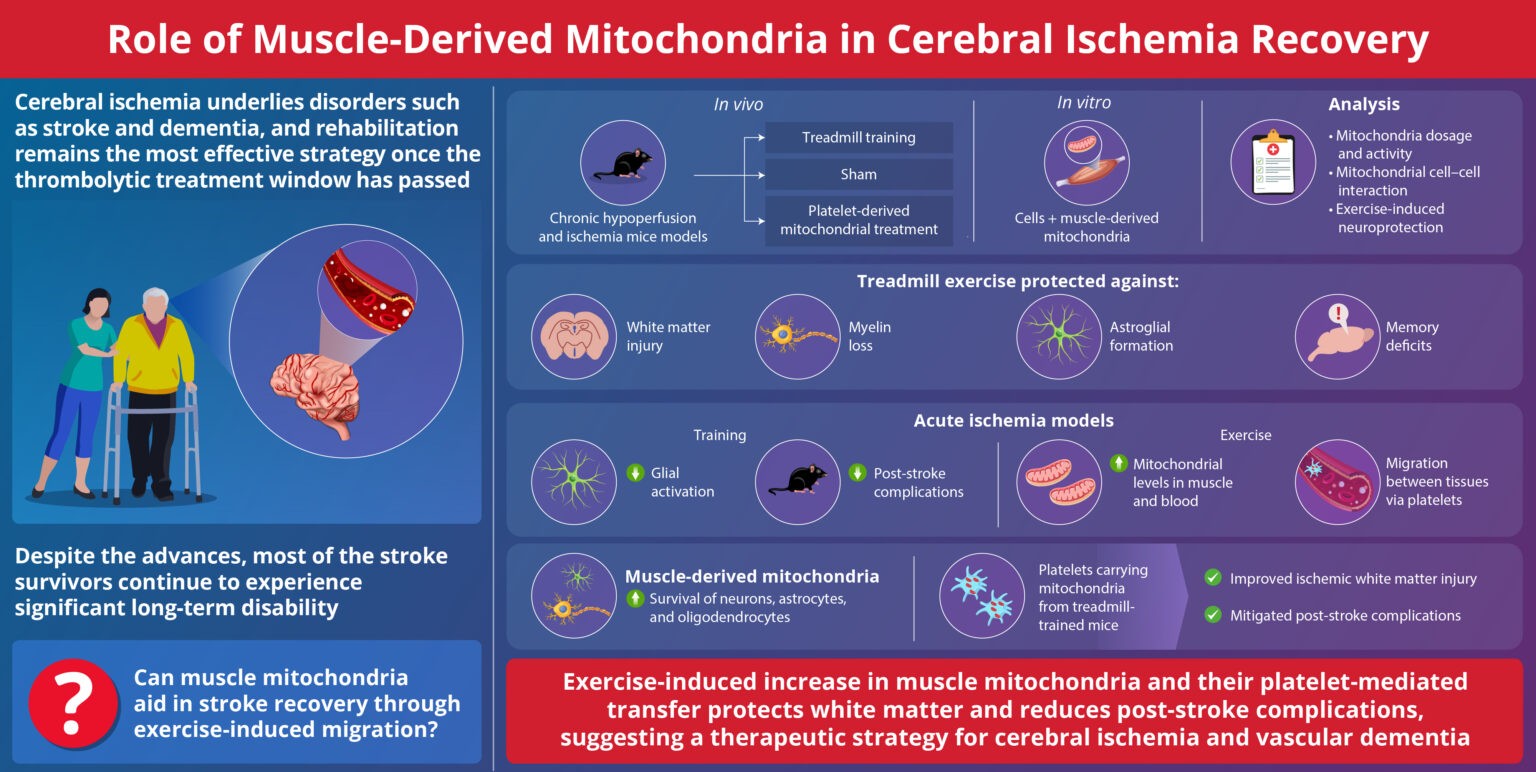
Mitochondrial dysfunction has been implicated in pregnancy-induced hypertension (PIH). The role of mitochondrial gene dysregulation in PIH, and consequences for maternal-fetal interactions, remain elusive.
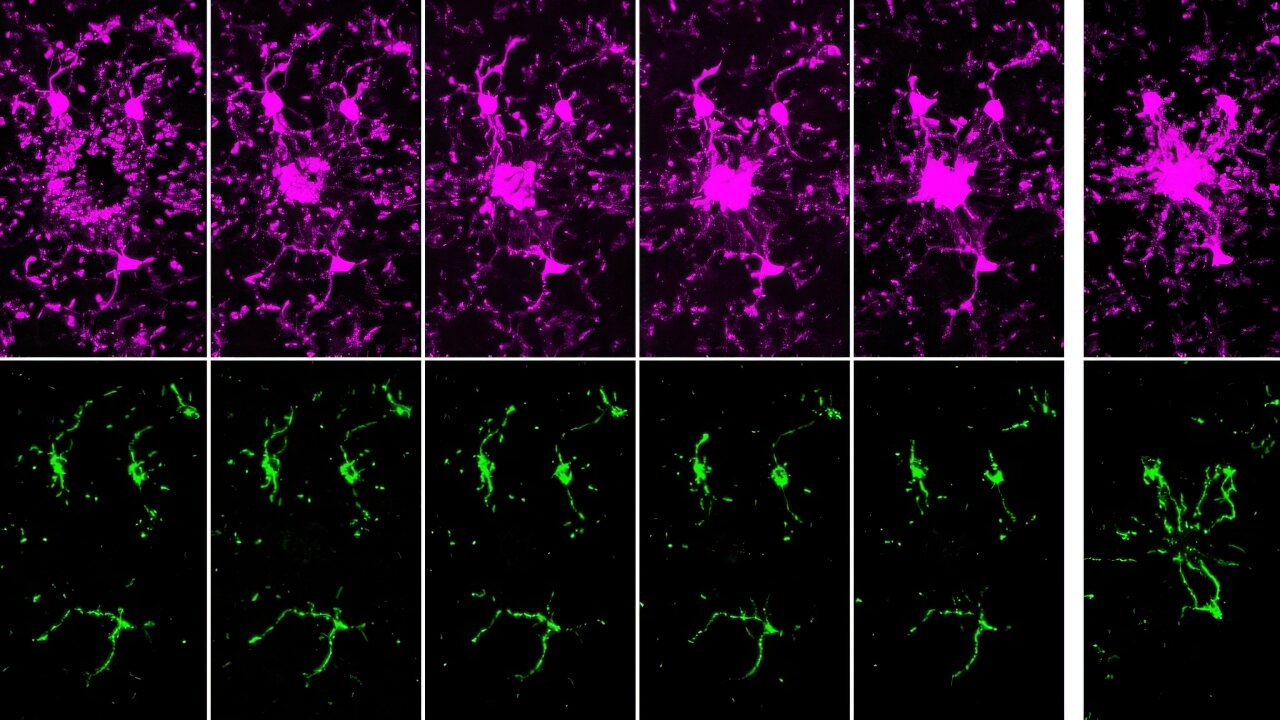
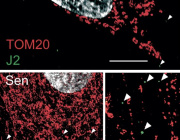
In their new study, Nicole R. Phillips (University of North Texas Health Science Center), Styliani Goulopoulou (Loma Linda University) and their colleagues investigated mitochondrial gene expression and dysregulation in maternal and placental tissues from pregnancies with and without PIH.
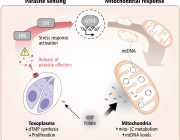
Further, they measured circulating mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) mutational load, an index of mtDNA integrity. Differential gene expression analysis followed by Time Course Gene Set Analysis (TcGSA) was conducted on publicly available high throughput sequencing transcriptomic data sets. Mutational load analysis was carried out on peripheral mononuclear blood cells from healthy pregnant individuals and individuals with preeclampsia.
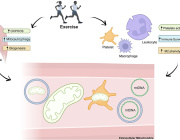
Thirty mitochondrial differentially expressed genes (mtDEGs) were detected in the maternal cell-free circulating transcriptome, whereas nine were detected in placental transcriptome from pregnancies with PIH. In PIH pregnancies, maternal mitochondrial dysregulation was associated with pathways involved in inflammation, cell death/survival, and placental development, whereas fetal mitochondrial dysregulation was associated with increased production of extracellular vesicles (EVs) at term. Mothers with preeclampsia did not exhibit a significantly different degree of mtDNA mutational load.
The reported findings support the involvement of maternal mitochondrial dysregulation in the pathophysiology of PIH and suggest that mitochondria may mediate maternal-fetal interactions during healthy pregnancy.
In summary, this study identifies aberrant maternal and fetal expression of mitochondrial genes in pregnancies with gestational hypertension and preeclampsia. Mitochondrial gene dysregulation may be a common etiological factor contributing to the development of de novo hypertension in pregnancy-associated hypertensive disorders.
Image credits: Ricci et al. Physiological Genomics (2023)
Targeting Mitochondria 2023, this October, will shed light on the latest discoveries related to mitochondria. Submit a related abstract.
Media contact:
World Mitochondria Society
This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
+33-1-5504-7755
Targeting Mitochondria 2023 Congress
October 11-13, 2023 - Berlin, Germany
wms-site.com