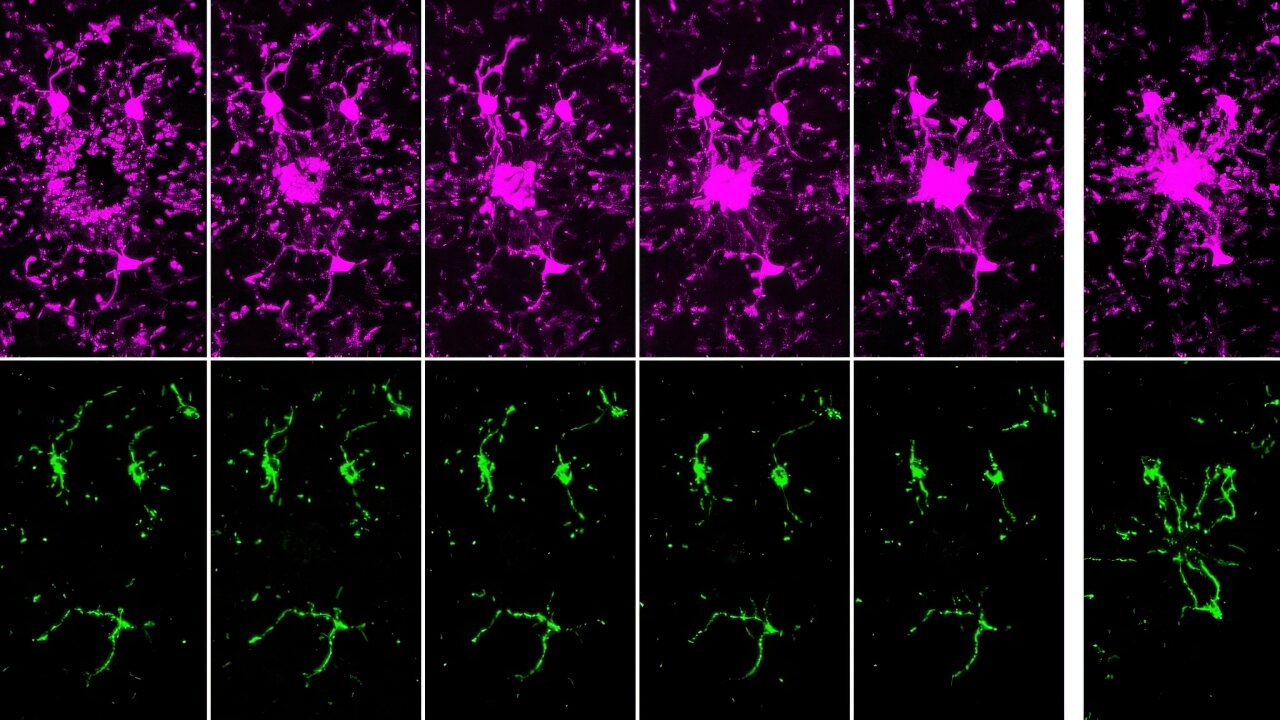
Tiny Messengers, Big Impact: Exosomes as Gatekeepers of Mitochondrial Function
The article titled “Extracellular vesicles: opening up a new perspective for the diagnosis and treatment of mitochondrial dysfunction” was published in the Journal of Nanobiotechnology on August 14, 2024.
Key Points:
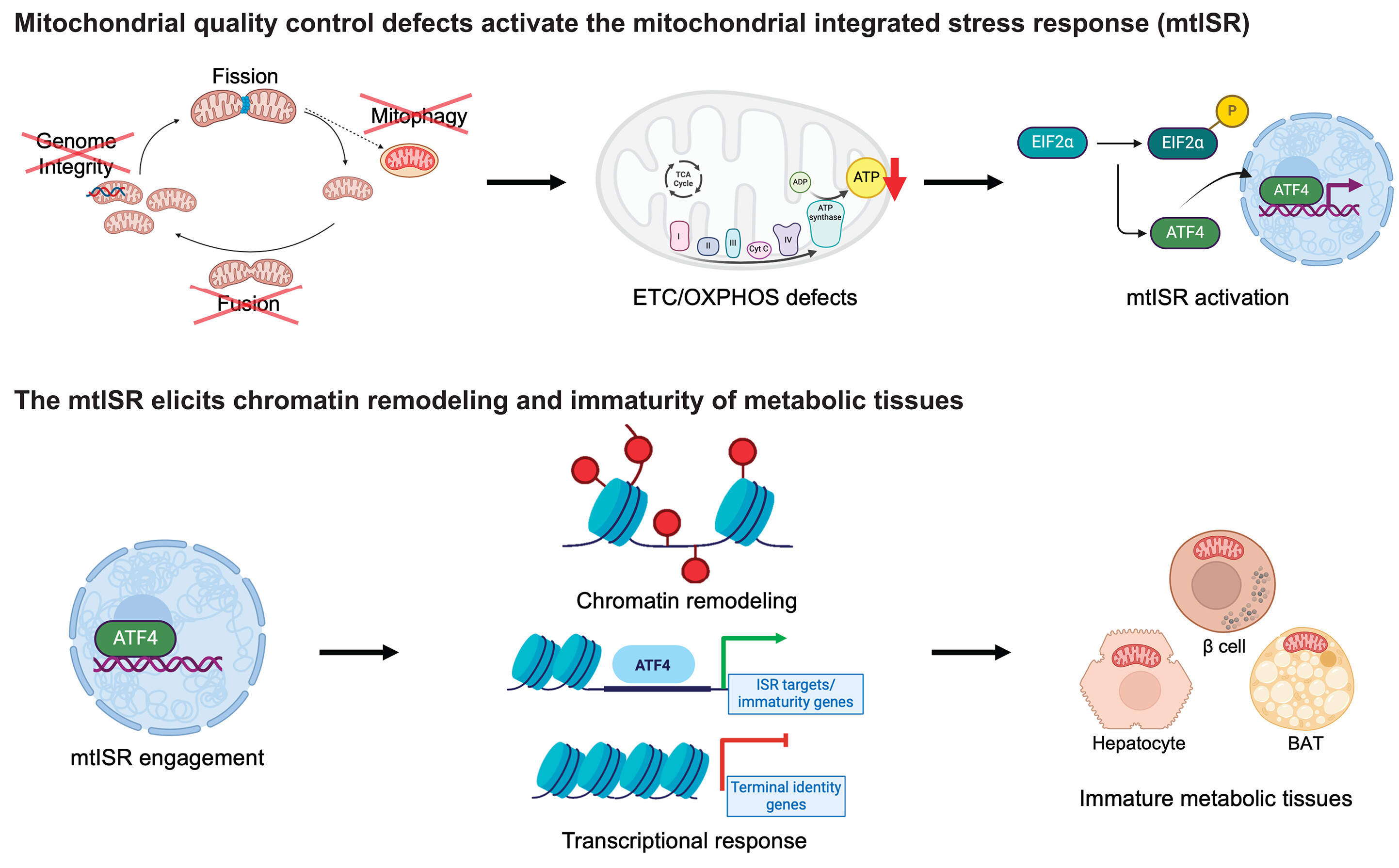
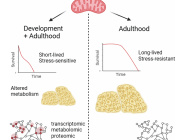
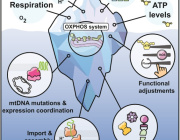
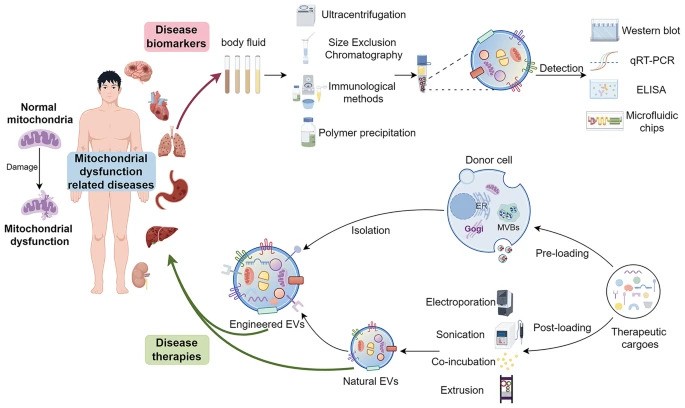
- Mitochondrial Dysfunction: Mitochondria are essential for energy production in eukaryotic cells. Disruptions such as oxidative stress, calcium imbalances, and mitochondrial DNA abnormalities can lead to mitochondrial dysfunction, contributing to various diseases.
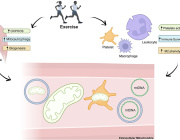
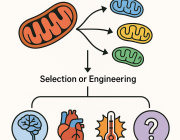
- Extracellular Vesicles (EVs): EVs are cell-derived nanovesicles that facilitate intercellular communication by transporting proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. They are categorized based on size into small EVs (sEVs, <200 nm) and large EVs (lEVs, >200 nm).
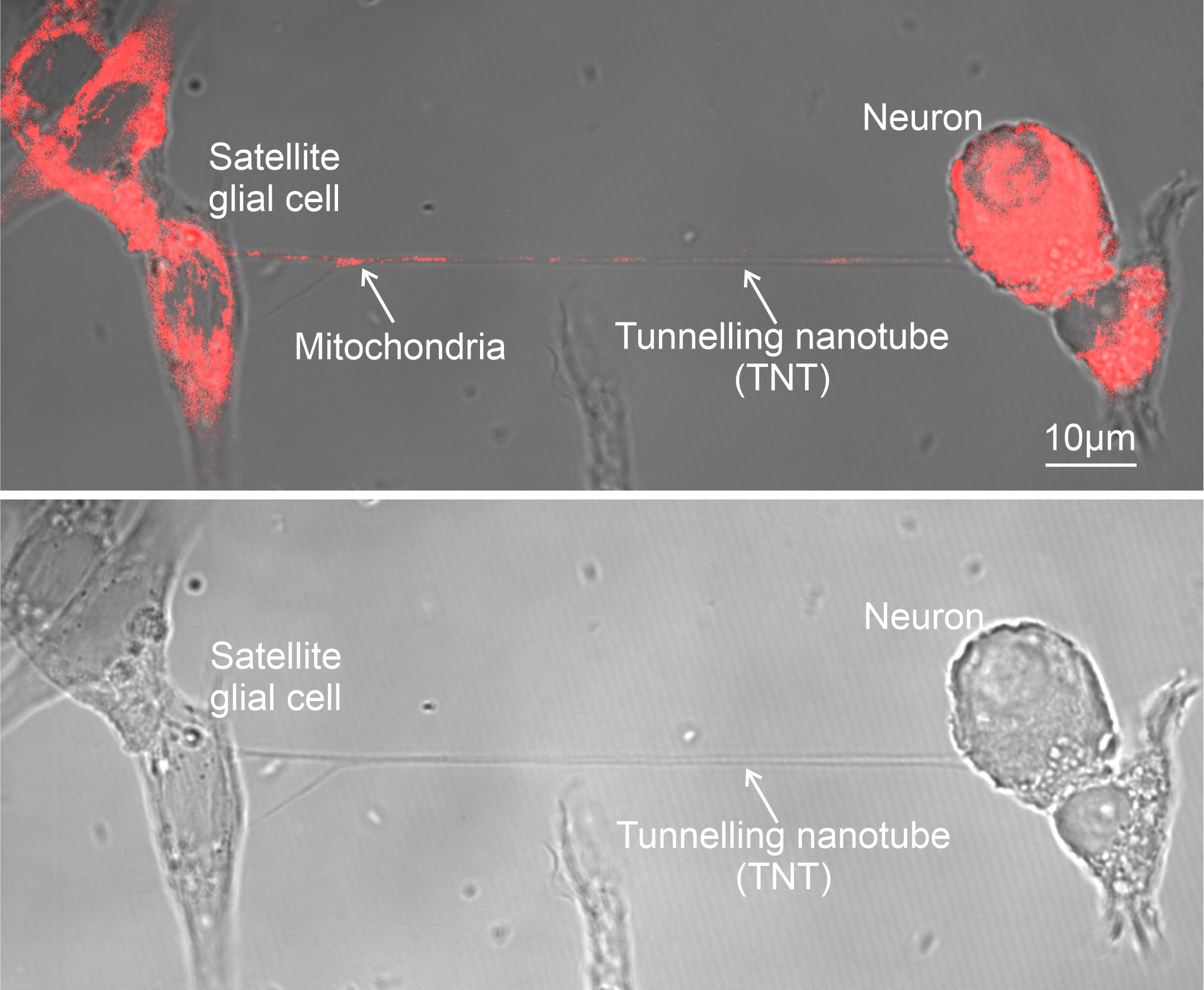
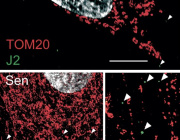
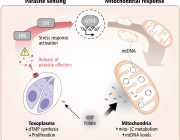
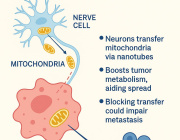
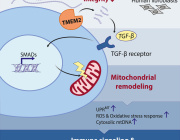
- EVs and Mitochondrial Components: Certain EV subtypes are enriched with mitochondrial components, including intact mitochondria. These EVs can transfer mitochondrial elements to recipient cells, influencing mitochondrial function.
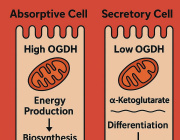
- Modulation of Mitochondrial Function: EVs can affect mitochondrial homeostasis, apoptosis, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation in target cells by delivering specific substances.
- Therapeutic Potential: Research is exploring the artificial modification of EVs as delivery vehicles for therapeutic agents targeting mitochondria, offering new avenues for treating conditions associated with mitochondrial dysfunction.
Perspective:
This review highlights the emerging role of EVs in modulating mitochondrial function, presenting innovative strategies for diagnosing and treating diseases linked to mitochondrial dysfunction. By leveraging the natural communication pathways of EVs, there is potential to develop targeted therapies that restore mitochondrial health, offering hope for conditions such as neurodegenerative diseases, cardiovascular disorders, and cancer. Future research should focus on understanding the mechanisms governing EV-mediated mitochondrial modulation and developing safe, effective EV-based therapeutic approaches.
Learn more in the full article.
© Image: Li, J., Wang, T., Hou, X. et al. J Nanobiotechnol22, 487 (2024).