Ketone Bodies: A New Approach to Brain Function and Neurodegenerative Diseases
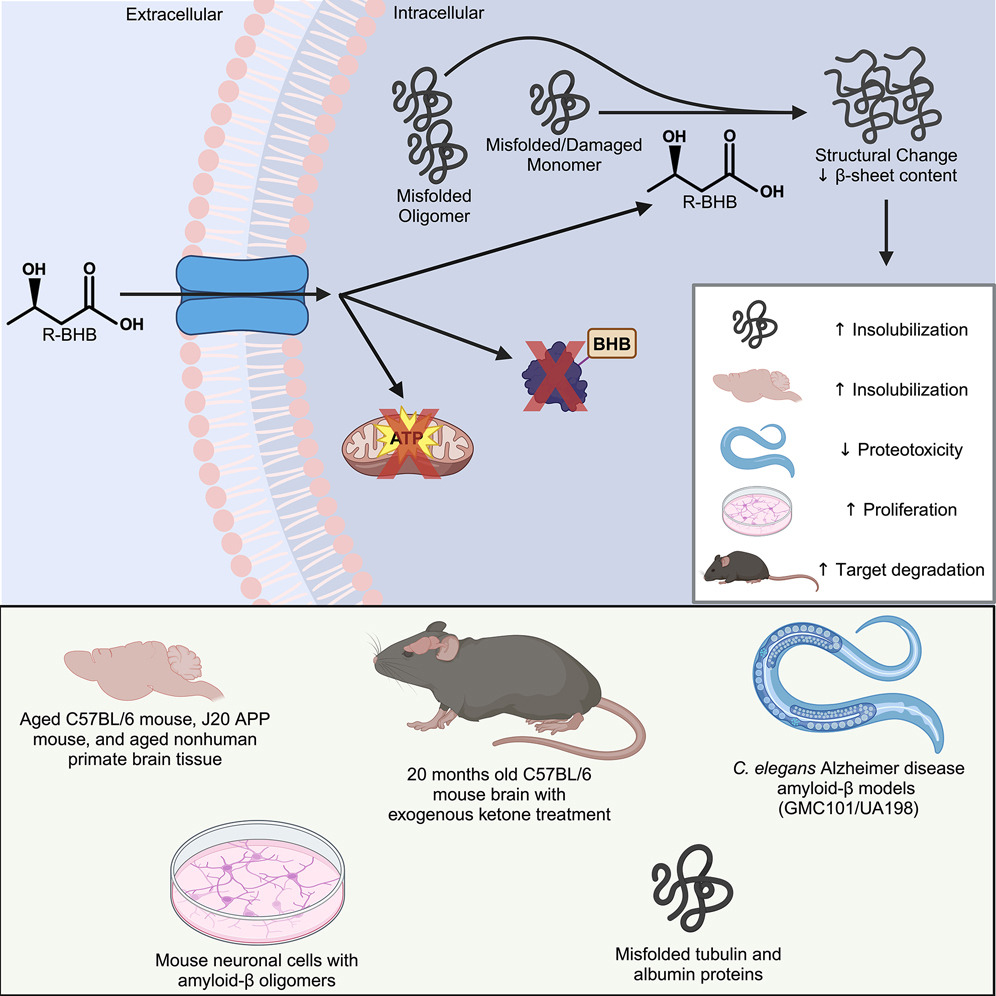
A recent study published in Cell Chemical Biology by researchers at the Buck Institute for Research on Aging has revealed intriguing new roles for ketone bodies, particularly β-hydroxybutyrate, in maintaining brain health. While ketone bodies are primarily recognized for their role in energy production, this research highlights their broader impact on mitochondrial function and protein homeostasis in the brain, offering promising insights for aging and neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s.
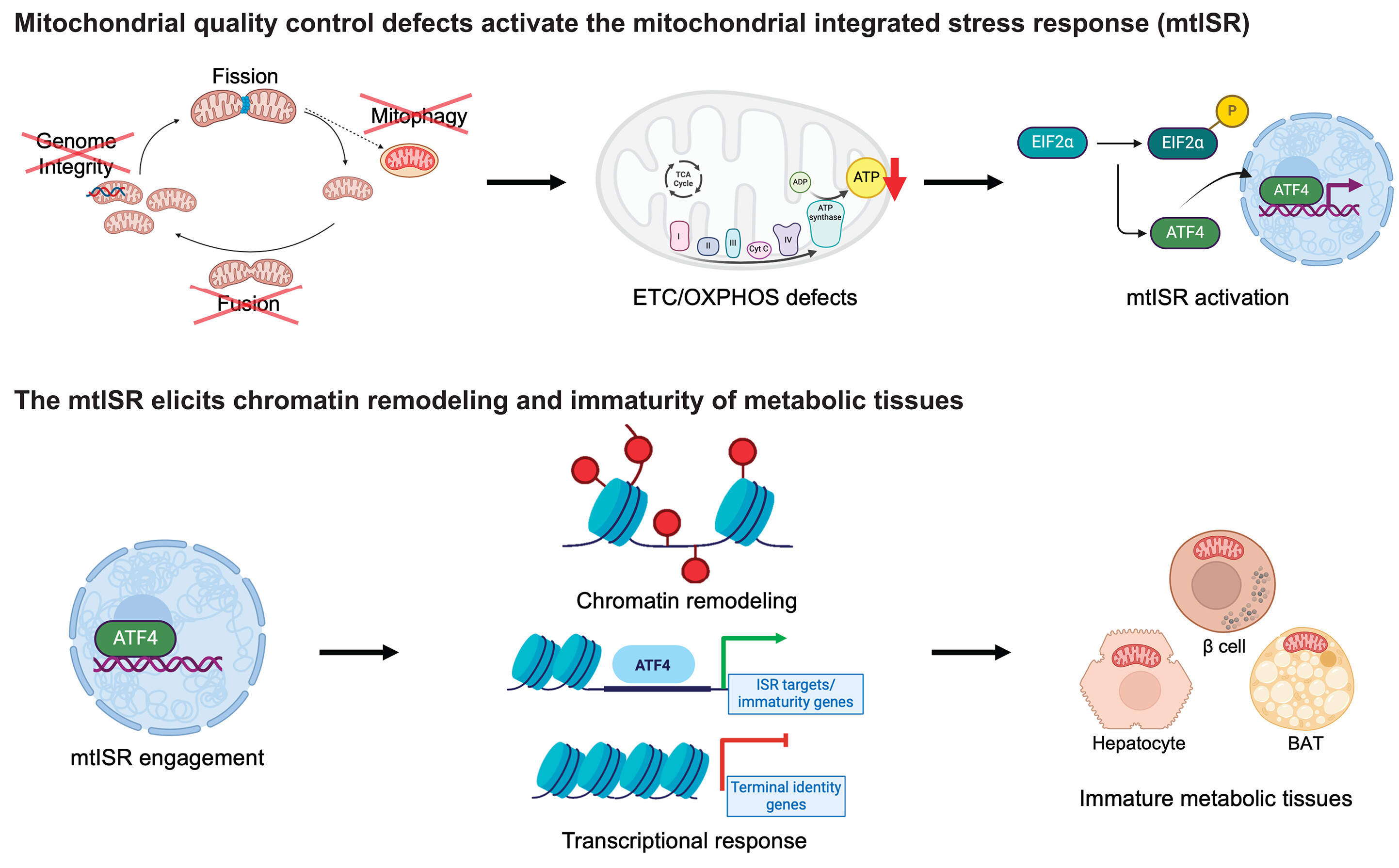
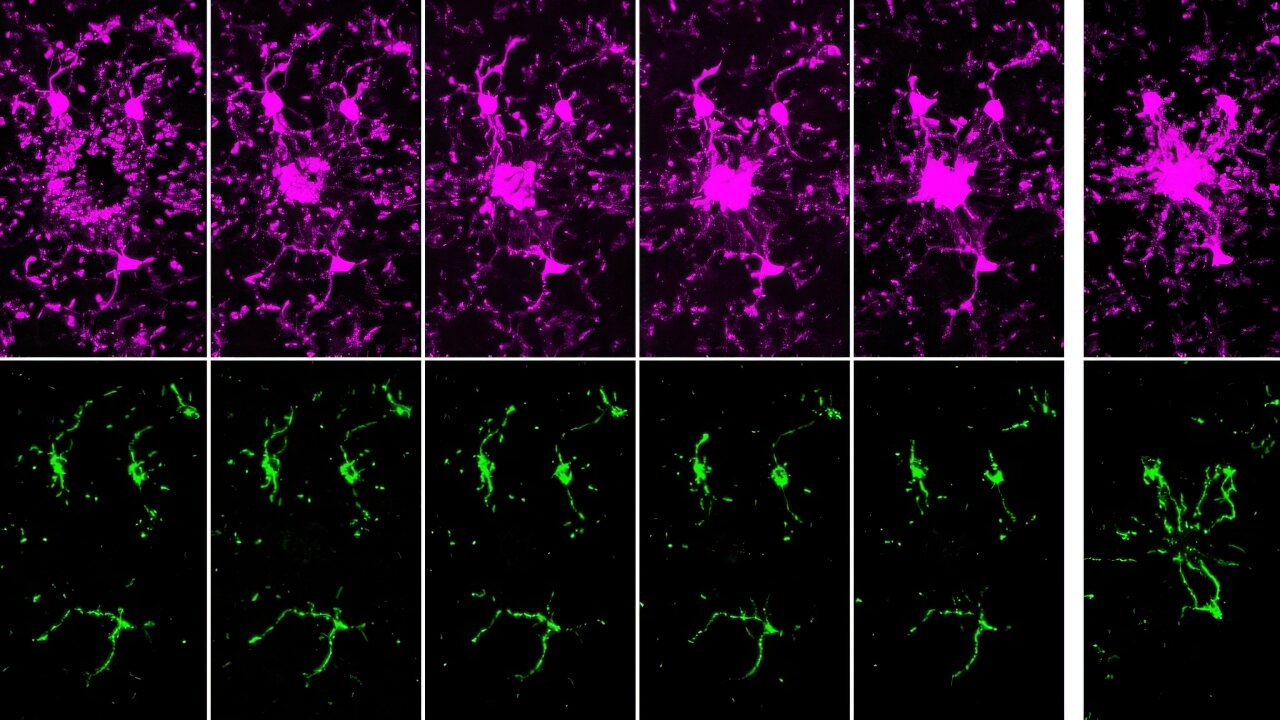
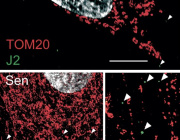
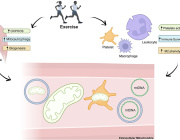
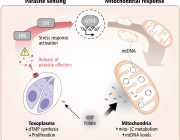
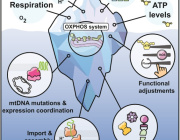
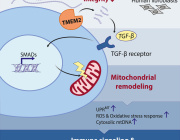
The study shows that β-hydroxybutyrate directly interacts with misfolded proteins in the brain, altering their structure and solubility to promote their clearance through autophagy. This process is crucial for supporting mitochondrial function, as it prevents the buildup of damaged proteins that can impair cellular health and energy production.
In addition, ketone bodies have a profound effect on protein quality control mechanisms within the brain. By influencing the proteome, ketones help enhance the clearance of dysfunctional proteins, ensuring that mitochondrial and cellular functions remain intact. This mechanism is vital for preserving the overall health of brain cells, especially as they age.
Experimental validation in animal models further supports these findings. When mice were fed ketone esters, the clearance of insoluble proteins was enhanced, preventing pathological aggregation. In nematodes expressing human amyloid beta, ketone treatment successfully reversed paralysis, suggesting a restoration of mitochondrial function and recovery from protein-induced damage.
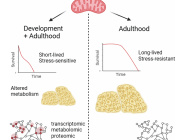
These findings open up new potential therapeutic avenues for brain aging and neurodegenerative diseases. By manipulating ketone body levels, it may be possible to support mitochondrial function and facilitate the removal of damaged proteins from the brain. This approach could serve as a powerful strategy to mitigate the effects of aging on the brain and provide a novel way to treat neurodegenerative diseases.
The research underscores the emerging role of ketone bodies as signaling molecules that help regulate protein homeostasis and mitochondrial health in the brain. As mitochondrial dysfunction is a central factor in many neurodegenerative diseases, this study paves the way for new therapeutic approaches aimed at boosting mitochondrial resilience and improving brain health.
Image Credits: Sid Madhavan, Buck Institute for Research on Aging