Mitochondrial Cybrids: Advancing Precision Oncology
About Dr. Anel :
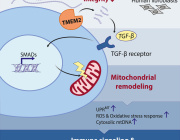
Dr. Alberto Anel, a leading scientist at the University of Zaragoza, Spain, specializes in mitochondrial research, cancer biology, and immunotherapy. His work explores how mitochondria influence cancer cell survival, treatment resistance, and immune system interactions.
Key implications of his research include enhancing cancer treatments by targeting mitochondria, advancing personalized medicine through cybrid models to assess mtDNA mutations, and developing new therapies for autoimmune diseases. His findings could lead to more effective treatments, improved patient outcomes, and precision medicine based on mitochondrial genetics. Mitochondrial cybrids continue to be a crucial tool in biomedical research, driving innovation in therapeutic strategies.
What is Mithochondria Cybrids ?
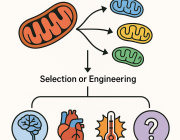
A cybrid (cytoplasmic hybrid) is a laboratory-engineered cell that contains the nuclear DNA (nDNA) from one cell and mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) from another. Scientists create cybrids to study the role of mitochondria in diseases such as cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and metabolic conditions.
Why Are Cybrids Important?
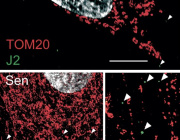
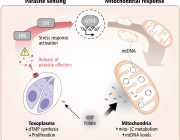
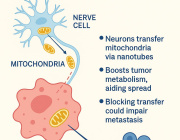
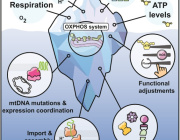
Mitochondria, often called the “powerhouses of the cell,” are crucial for energy production and cellular health. However, mutations in mtDNA can contribute to cancer progression, drug resistance, and other diseases.
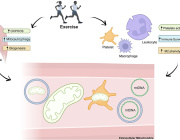
Cybrids allow researchers to isolate the effects of mitochondrial DNA changes without interference from nuclear DNA. This makes them a powerful tool for biomedical research in understanding how mitochondria impact health and disease.
Applications of Mitochondrial Cybrids
- Disease Modeling: Cybrids help scientists study mitochondrial diseases by isolating the effects of specific mtDNA mutations. For example, they have been used to investigate mitochondrial dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease.
- Drug Testing: By introducing different mtDNA haplotypes into a consistent nuclear background, cybrids help evaluate how genetic variations affect cellular responses to drugs. This is useful for predicting adverse drug reactions and treatment efficacy.
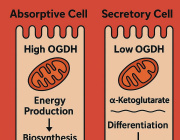
- Metabolic Research: Cybrids provide insights into how mtDNA variations influence metabolism, particularly in conditions affecting energy production and mitochondrial function.
Significance of Mitochondrial Cybrids
By enabling the study of mtDNA’s role in cellular function without the confounding effects of nuclear DNA, cybrids are crucial for:
- Understanding Mitochondrial Diseases: They allow researchers to directly assess how mtDNA mutations contribute to disease pathology.
- Personalized Medicine: Cybrid models help predict individual responses to medications based on mitochondrial genetics, paving the way for tailored therapeutic approaches.
- Evolutionary Studies: Cybrids offer a platform to study the compatibility and functional impact of introducing mtDNA from different species or populations into a shared nuclear environment.